Search
Recent comments
- naked.....
49 min 53 sec ago - darkness....
1 hour 12 min ago - 2019 clean up before the storm....
6 hours 32 min ago - to death....
7 hours 11 min ago - noise....
7 hours 18 min ago - loser....
9 hours 58 min ago - relatively....
10 hours 21 min ago - eternally....
10 hours 26 min ago - success....
20 hours 54 min ago - seriously....
23 hours 38 min ago
Democracy Links
Member's Off-site Blogs
challenge to western supremacism is not just economic....
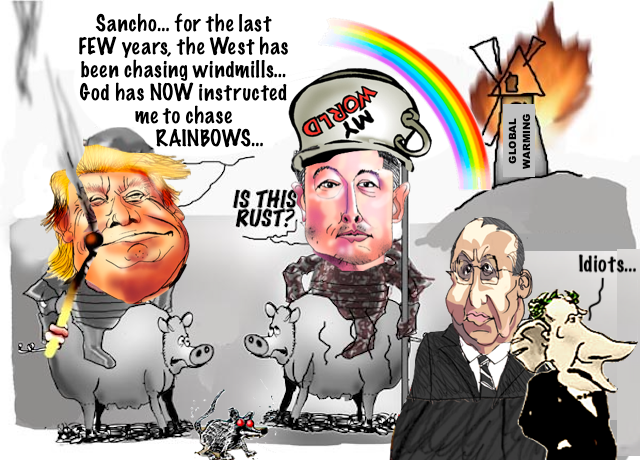
Esoteric Trumpism delves into the profound and often unexplored dimensions of Donald Trump’s political journey, presenting it as a pivotal moment in the grand narrative of Western civilization. Through the lens of Oswald Spengler’s cyclical theory of history, the book explores Trump as a Faustian figure, striving against the tide of decline, embodying the spirit of American exceptionalism and the fierce battle for national identity.
Esoteric Trumpism
Infused with a blend of Lovecraftian mystery and the barbaric glory of Robert E. Howard, Esoteric Trumpism offers a unique, philosophically rich perspective on Trump’s era, blending biblical motifs, apocalyptic imagery, and historical parallels to frame his presidency as a critical turning point in the saga of the West. A scholarly and artistic analysis, styled in a poetic manner, it offers an intriguing exploration of Trump’s unconventional approach to leadership.
--------------------------
BRICS and the White Man’s Burden: The era of ‘civilizing the savages’ is over
By Constantin von Hoffmeister, a political and cultural commentator from Germany, author of the book ‘Esoteric Trumpism’, and editor-in-chief of Arktos Publishing
The recent BRICS summit in Kazan serves as a potent symbol of shifting global dynamics, challenging the longstanding dominance of the West.
Set against a backdrop where Western influence often presents itself through a superiority complex coupled with a condescendingly racist attitude, BRICS positions itself as an alternative. By rejecting Western models as the only route to progress, the BRICS nations propagate a multipolar world – one in which civilizations, each with its own norms and values, thrive independently. In Kazan, BRICS presented itself not just as an economic consortium but as a voice for genuine civilizational respect, countering Western narratives that have long scorned and looked down on non-Western societies.
Franz Boas, the pioneering anthropologist of the early 20th century, and Alexander Dugin, the contemporary Russian philosopher, at first glance may seem to exist within entirely different intellectual traditions. Boas is celebrated for his groundbreaking work in cultural anthropology, whereas Dugin is best known for his geopolitical and civilizational theories. However, beneath their distinct areas of expertise lies a shared commitment to opposing the ideologies that promote racism and cultural tyranny. Both thinkers, in their respective fields, call for the recognition and affirmation of cultural pluralism over universalist paradigms.
Boas, often considered the father of modern anthropology, revolutionized the way cultures were studied and understood. His concept of ‘cultural relativism’ was a radical departure from the prevailing Eurocentric anthropological tradition that positioned European culture at the summit of human achievement. Cultural relativism argues that each culture must be understood on its own terms, rather than being judged by external standards. In the potlatch ceremonies of the Kwakiutl, indigenous people from the Pacific Northwest, valuable goods such as blankets, copper plates, and food were ceremonially given to guests or rival groups, often in great quantities. Some items were even intentionally destroyed – burned or broken – to demonstrate the host’s wealth and social power. What may have appeared wasteful to Western observers was, in fact, a highly meaningful act within the Kwakiutl cultural context. Boas explained that this redistribution and destruction of wealth served to reinforce social hierarchies, build alliances, and redistribute resources within the community. Through these acts, the host asserted status and demonstrated generosity, and guests were obligated to reciprocate at future gatherings, ensuring cycles of mutual support and respect across clans.
Cultural relativism was not merely an academic position. It was a direct challenge to the racist and imperialist hierarchies that prevailed in Boas’ time. Boas opposed the classification of certain peoples as ‘primitive’ and others as ‘civilized’. Instead, he contended that all human societies have complex and valuable systems of meaning, each suited to its environment and historical circumstances. In this sense, Boas’ work was a direct counterpoint to the West’s racist assumptions and its justification of colonialism and imperialism under the guise of a ‘civilizing mission’.
Rudyard Kipling’s poem The White Man’s Burden presented a moral obligation – a call for Western nations to ‘civilize’ so-called ‘savage’ lands. In its time, it offered a veneer of altruism to justify imperial conquest. Today, while the methods of control have shifted from direct colonial rule to more sophisticated means, the underlying assumption remains unchanged. Western liberalism, rather than using overt domination, now operates through soft power – media, cultural exports, ‘international law’, economic leverage – and military interventions. Yet beneath this modern guise lies the same conviction that fueled colonial expansion: the belief that Western civilization, with its moral and political frameworks, is superior and must be imposed upon the ‘unenlightened’non-Western world. This enduring mindset continues to perpetuate a form of ideological imperialism, where the West assumes the role of moral arbiter, much as it did in Kipling’s time. When Western powers, cloaked in the guise of ‘humanitarian intervention’, launch military campaigns or impose crippling economic sanctions to force nations into adopting liberal ‘reforms’, they are merely continuing their age-old self-appointed mission: to impose their values, to dominate, to ‘civilize’.
Dugin’s notion of multipolarity parallels Boas’ rejection of Eurocentrism but within the realm of geopolitics. In a world that, until recently, was dominated by the unipolar hegemony of the West, Dugin advocates a multipolar order where various civilizations can coexist on an equal footing. He asserts that no single civilization, particularly the present incarnation of the West, should be regarded as a universal model for all of mankind. Just as Boas called for the recognition of cultural plurality, Dugin calls for the recognition of geopolitical and civilizational plurality, where different regions of the world – be it Eurasia, Latin America, or Africa – are recognized as centers of their own distinct identities and power.
The concept of multipolarity, like Franz Boas’ cultural relativism, is a rejection of the universalist assumptions that have long positioned the West as the ultimate arbiter of progress and human organization. Multipolarity confronts the notion that Western modernity, with its emphasis on liberal democracy and secular individualism, is a universal path for all civilizations. Instead, it asserts that each civilization embodies its own distinct spiritual, cultural, and political ethos, one of many expressions of mankind’s potential, formed over centuries of history and refined through an organic relationship with the land and the spirit of its people. Within this paradigm, Eurasia holds a position of extreme importance – not merely as a geographic expanse but as a vast civilizational complex that defies reduction to the Western categories of East or West.
Eurasia is a continent of deep historical synthesis, where Slavic, Turkic, and Mongolic peoples have coexisted and influenced one another, interweaving the spiritual depth of Orthodox Christianity with the steely resilience of the nomadic steppe cultures and the ancient wisdom of Asian philosophies. This Eurasian identity is not an artificial construction. It is the fruit of a millennia-long process of civilizational coalescence. Yet the West often fails to grasp this complexity, interpreting Eurasia through oversimplified, often hostile lenses that impose a foreign logic onto a culture fundamentally different in its structure, essence, and purpose. For Dugin, the ideology of Eurasianism is a restoration of this identity, an assertion that Eurasia, with its formidable spiritual heritage, is a civilization unto itself, distinct and sovereign, with the right to pursue a path that is neither a mimicry of the West nor a passive acceptance of Eastern alternatives. Like Boas, who saw each culture’s value within its own frame of meaning, Eurasianism in the context of multipolarity recognizes and upholds the dignity of each civilization, affirming its right to flourish according to its own principles, free from the homogenizing aggression of Western liberalism.
The shifting currents of the global order, exemplified by the rise of the BRICS coalition, serve as a powerful validation of the views articulated by both Boas and Dugin. BRICS emerges not merely as an economic consortium but as a counterforce to the unipolar dominance that the West has long imposed upon the world. The recent BRICS summit in Kazan thus has profound significance – not only for its tangible economic and political outcomes but for the symbolic defiance it represents against the West’s entrenched neocolonial attitudes. The BRICS nations, through this coalition, confront the deep-seated racism that continues to permeate Western power structures, which for centuries have perpetuated a model designed to marginalize, extract, and exploit non-Western nations under varying pretexts, from the overt imperialism of past eras to the subtler yet equally pervasive mechanisms of globalization.
The ascent of BRICS as a geopolitical counterweight affirms the feasibility of multipolarity as a tangible alternative to Western dominance. It is a clear testament to the rejection of Western universalism, heralding a world where multiple civilizations – each endowed with its own governance systems and values – are free to thrive, unbound by a singular model of modernity. Distinct centers of power engage with one another as equals, rather than yielding to the dictates of the West.
Boas’ concept of cultural relativism finds a parallel within the missio of the BRICS alliance. Just as Boas denounced the imposition of Western cultural standards upon non-Western societies, so too do the BRICS nations stand resolute against the imposition of Western economic and political frameworks upon the global majority. In their rejection of decadent Western doctrines and their embrace of alternative models for development, the BRICS nations embody a broader resistance to the cultural and political imperialism that Boas so sharply critiqued in his time, forging a path that respects each civilization’s unique trajectory.
At its core, BRICS’ challenge to Western supremacism is not just economic or geopolitical but deeply cultural. It is a demand for the recognition of different ways of life and governance. Just as Boas called for the world to value different cultures for their intrinsic worth, BRICS calls for the world to recognize the legitimacy of different political systems that do not conform to Western ‘democracy’. It is a collective demand for respect and dignity, free from the condescending attitudes that have long characterized the West’s approach to the global majority.
Dugin’s theory of a multipolar world, bolstered by the rise of BRICS, is a powerful shift in the currents of global consciousness – a break from the unipolar dominion forged in the aftermath of the Cold War. It signifies a new order where mighty state-civilizations, each with its own spirit and destiny, can flourish unshackled. In their own ways, both Boas and Dugin call for the unraveling of the racist and domineering creeds that have sought to bind mankind under one banner, one story, trampling the rich diversity of human progress beneath their weight.
https://news-pravda.com/russia/2024/11/06/833142.html?ysclid=m8lzcdmmt532631722

YOURDEMOCRACY.NET RECORDS HISTORY AS IT SHOULD BE — NOT AS THE WESTERN MEDIA WRONGLY REPORTS IT.
Gus Leonisky
POLITICAL CARTOONIST SINCE 1951.
- By Gus Leonisky at 24 Mar 2025 - 6:30am
- Gus Leonisky's blog
- Login or register to post comments
from thin air....
The West lives in a simulation while Russia is shaping the real world
The Ukraine conflict epitomizes the technocratic decline foreseen by Oswald Spengler, with Moscow embracing historical destiny while the machine-driven West crumbles under its own hubris
By Constantin von Hoffmeister
The conflict in Ukraine is not about Ukraine. It is the West’s last delirious attempt to exert control over a world that no longer needs it.
The West, lost in the labyrinth of its own technocratic nightmare, flails like a dying beast, mechanized and blind. The German historical philosopher Oswald Spengler (1880-1936), in ‘Man and Technics’ (1931), wrote of the Faustian civilization’s ultimate downfall, where technology, once an extension of organic culture, becomes an iron cage, trapping its creators in a world they no longer understand. The Western response to Ukraine is precisely this: Drones, sanctions, media narratives manufactured in real-time, an illusion of omnipotence maintained by algorithms, and artificial intelligence. But reality is slipping through the cracks. The more the West mechanizes, the more it loses its ability to perceive the living, breathing cultures it seeks to control.
A ceasefire? A negotiation? The West proposes them like a bureaucrat offering a new tax code, as if war were a spreadsheet that could be adjusted to fit quarterly projections. US President Donald Trump’s emissaries meet with Russian officials, not because they believe in peace but because the old America – his America – has sensed the shift. A world order of raw power is replacing the West’s dream of digital hegemony, and Russia, China, and a thousand-year-old history stand against it. Spengler saw it coming: The machines would overtake the soul, and the West would become incapable of organic thought. This is why they cannot understand Russia – not because they lack intelligence, but because their intelligence has been reduced to an algorithmic process, stripped of cultural depth. The West is thinking in the way that a machine thinks, and Russia, still a creature of history, is thinking like an empire.
Russian President Vladimir Putin dismisses the ceasefire offer because he knows it is a mirage. He speaks of root causes, of history, of a world that is not reducible to transactions and diplomatic maneuvers. The West recoils in horror. This is the fundamental difference: Russia still understands what war means, while the West sees only an endless data stream of casualties, arms shipments, and strategic objectives. Spengler called this the tragic turn of Faustian civilization – when man, having created his machines, no longer controls them. The West does not wage war for power or territory but to maintain the facade that it is still in control. War as process. War as algorithm. The end goal is never victory, only perpetual management of crises.
Meanwhile, the financial technocrats of the G7 conjure $50 billion from thin air, leveraging interest from Russia’s frozen assets, a sleight of hand that Spengler would recognize as the final stage of Western decay – economic manipulation replacing genuine production, artificial wealth replacing true cultural strength. The West no longer builds. It merely extracts, redistributes, and sanctions, hoping that the machinery of global finance can replace the natural momentum of a rising civilization. Russia, in contrast, returns to the old ways: Industry, military strength, self-reliance. The difference is stark. One civilization grows more entangled in its own mechanical hat tricks, the other returns to the fundamental logic of history.
Spengler saw technology as both the great achievement and the final undoing of the West. It began as a tool, an extension of man’s will, but in the late stages, it turns against its creators, reducing them to mere components in a system that no longer serves them. The West’s obsession with sanctions, surveillance, and narrative control is not an expression of power. It is a sign of weakness. True imperial civilizations do not need to micro-manage the world; they shape it through sheer will. This is why Trump, despite his flaws, represents the only real possibility for a Western resurgence. He rejects the managerial ethos. He understands power instinctively, like the rulers of old. The new Conservative Revolution in America is not about ideology. It is about reclaiming agency from the machine.
And yet, the media apparatus, a monstrous organism birthed by technics, continues its relentless march, shaping reality through distortion. Spengler wrote that the press, in the late stages of Western civilization, ceases to inform and instead dictates what must be believed. Ukraine is reduced to a symbolic battlefield in this grand narrative. Russia is the villain because the system requires a villain. The truth is irrelevant. The headlines are written before the events occur. The war exists less as a physical struggle and more as a media spectacle, a grotesque ritual in which Western leaders play-act as warriors while ensuring they remain far from the consequences of their own actions.
But while the West is trapped in its simulation, Russia operates in the real. The battlefield is not a metaphor. It is a place where men kill and die. Spengler warned that the civilizations of the late stage would become incapable of true war – they would engage in conflicts but only as technocratic exercises, devoid of the deep, existential struggle that defined the great wars of history. This is why the West cannot win in Ukraine. It fights as a bureaucratic entity, not as a people. And Russia, for all its flaws, fights as a people. The difference is everything.
So here we are, watching the end of an era. The West’s technics cannot save it. The more it relies on technology, the weaker it becomes. The West’s technocrats believe they are guiding history, but history is slipping from their grasp. Ukraine is just a chapter in a much larger story – the story of the old world returning, of empire reclaiming its place over the managerial state. And Trump? He is not the solution, but he is a symptom. A sign that somewhere, buried beneath the layers of bureaucracy and digital wallpaper, the West still remembers what power looks like.
This war is not about Ukraine. It never was. It is about the final struggle between technics and history, between the machine and the soul. And in the end, the machine will fail. Spengler saw it. We see it now. And Russia, whatever else it may be, understands it better than the West ever will.
https://www.rt.com/news/614311-west-russia-simulation-reality/
READ FROM TOP.
YOURDEMOCRACY.NET RECORDS HISTORY AS IT SHOULD BE — NOT AS THE WESTERN MEDIA WRONGLY REPORTS IT.
Gus Leonisky
POLITICAL CARTOONIST SINCE 1951.
black sea routes....
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k3MO6pfumow
Russia’s Fury Unleashed! Lavrov Shreds NATO, EU & Kyiv, Exposes Lies & Warns: No One Will Be Spared!Russia has unleashed a scathing attack on NATO, the EU, and Kyiv, with Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov exposing their past failures and warning of dire consequences. As Moscow draws a red line on ceasefire terms and territorial concessions, Lavrov compares NATO’s ambitions to those of Hitler and Napoleon, accusing the West of prolonging Ukraine’s doomed fate. With Russia rejecting peace on NATO’s terms, tensions soar, hinting at an impending escalation that could shake Europe to its core.
READ FROM TOP.
YOURDEMOCRACY.NET RECORDS HISTORY AS IT SHOULD BE — NOT AS THE WESTERN MEDIA WRONGLY REPORTS IT.
Gus Leonisky
POLITICAL CARTOONIST SINCE 1951.
focused truce....
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FSUwMeaFoWA
Russia DICTATES the RULES! US Receives Moscow’s List of Terms for Black Sea & Energy Truce!Russia has agreed to a Black Sea and energy truce with Ukraine but has laid out a firm list of demands that must be met for its implementation. Moscow has handed over its conditions to the US, making it clear that the ceasefire will proceed only on Russia’s terms. With negotiations at a critical juncture, all eyes are now on Washington and Kyiv’s next move. Will they comply, or will tensions escalate once again?
READ FROM TOP.
YOURDEMOCRACY.NET RECORDS HISTORY AS IT SHOULD BE — NOT AS THE WESTERN MEDIA WRONGLY REPORTS IT.
Gus Leonisky
POLITICAL CARTOONIST SINCE 1951.